
BackToCAD Technologies LLC | Artificial Intelligence and Software Developing | Clearwater, USA; Stuttgart, Germany | Kazmierczak® Company
Understanding dimensioning concepts
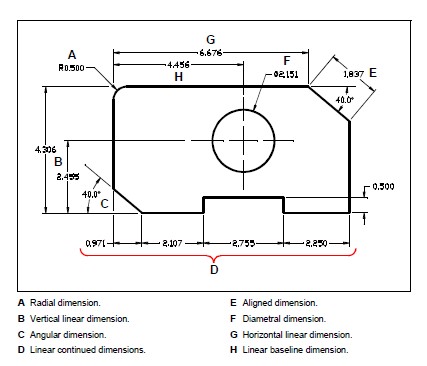
You can create five basic types of dimensions: linear, angular, radial, diametral, and ordinate. You can create dimensions for existing entities by selecting them, or you can create dimensions by selecting points within a drawing. For example, you can create a linear dimension either by selecting the entity to be dimensioned or by specifying the first and second extension line origins.
When you create a dimension, the program draws it on the current layer, using the current dimension style. Each dimension has a corresponding dimension style, which controls the appearance of the dimension, such as the types of arrowheads, text style, and colors of various components.
You can modify existing dimension styles by changing one of the dimension variable settings and then updating the dimension style to reflect the new settings.
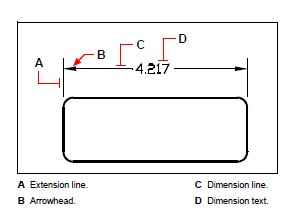
Each dimension you create consists of several parts. A dimension line shows where a dimension begins and ends. When you create an angular dimension, the dimension line is a dimension line arc that subtends the measured angle.
Extension lines, also called projection lines, are lines that extend away from the entity for which you are creating a dimension, so that you can place the dimension line away from the entity. Arrowheads form the termination at each end of the dimension line.
Dimension text contains the measured dimension and can also include prefixes, suffixes, tolerances, and other optional text. As you insert dimensions, you can control the dimension text and specify its position and orientation.
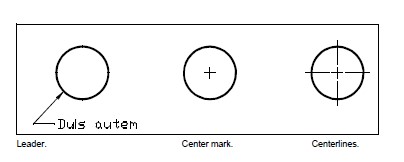
Dimensions can also contain other optional components. A leader is a line leading from a feature of the drawing to an annotation. Leaders begin with an arrowhead, and you can use them to place a dimension away from the dimension line or to add notes. When you create a radial dimension, you can add a center mark, which is a small cross that marks the center of a circle or an arc, or you can add centerlines, which are crossing lines that extend out from the center of a circle or an arc.
Dimensions can be one of three types:
- Associative — A dimension is linked with the entities it measures. If the entities being measured by the dimension are modified, the dimension is updated automatically. Newly created dimensions are associative when DIMASSOC is set to 2 (default) and created using entity snaps.
- Non-associative — A dimension is not linked with the entities it measures. If the entities being measured by the dimension are modified, the dimension is not updated automatically. Newly created dimensions are non-associative when DIMASSOC is set to 1.
- Exploded — Dimensions are created as separate entities, not a single dimension entity. Newly created dimensions are exploded when DIMASSOC is set to 0.
© Copyright 2021 BackToCAD Technolgies LLC . All rights reserved. Kazmierczak® is a registered trademark of Kazmierczak Software GmbH. CADdirect 2022 is a trademark of Expert Robotics Inc. Print2CAD and CAD2Print are Trademarks of BackToCAD Technologies LLC. DWG is the name of Autodesk’s proprietary file format and technology used in AutoCAD® software and related products. Autodesk, the Autodesk logo, AutoCAD, DWG are registered trademarks or trademarks of Autodesk, Inc., and/or its subsidiaries and/or affiliates in the USA and/or other countries. All other brand names, product names, or trademarks belong to their respective holders. This website is independent of Autodesk, Inc., and is not authorized by, endorsed by, sponsored by, affiliated with, or otherwise approved by Autodesk, Inc. The material and software have been placed on this Internet site under the authority of the copyright owner for the sole purpose of viewing of the materials by users of this site. Users, press, or journalists are not authorized to reproduce any of the materials in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including data storage and retrieval systems, recording, printing or photocopying.